Gut microbiome
About microbiome
There is no life or health without the gut microbiome
What does the gut microbiome mean?
The gut microbiota is a complex of microorganisms that colonize the human gastrointestinal track, mainly the intestines.
Why is gut microbiota is crucial for human health?
The gut microbiota constitutes an integral part of the human body, and is referred to as the “super organ” that affects the functioning of the human body.
Is there a difference between the gut microbiota and gut microbiome?
Gut microbiome – means the genetic material of microbiota, but now both terms can be used interchangeably.
The gut microbiota in numbers

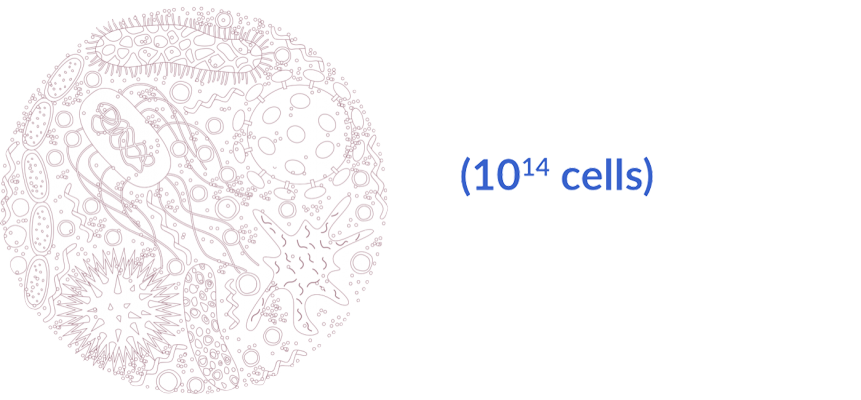


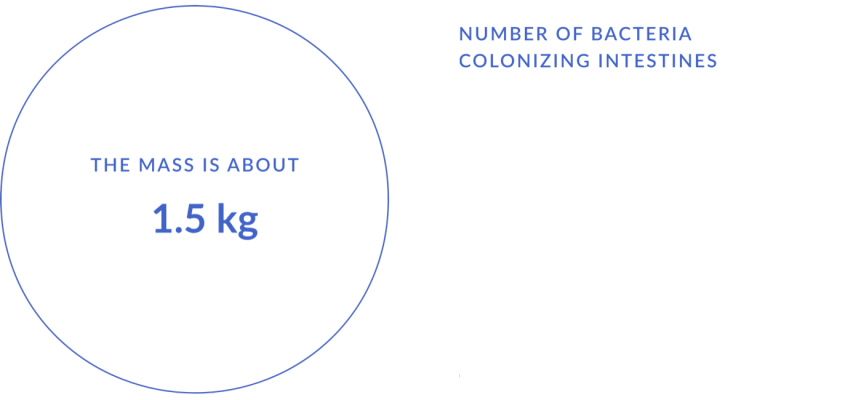
The role of the gut microbiome
- It supports the functioning of the digestive tract: peristalsis, enzyme production, digestion and absorption of lipids, minerals (Ca2+) etc.
- It produces vitamins – mainly vitamins K and B
- It forms the intestinal barrier – prevents leaky gut, protects against allergen and toxin penetration
- It supports the functioning of the immune system – direct anti-pathogenic activity, activation of antibodies
- It activates the production of antibodies, including mucosal secretory IgA antibodies – the first line of immune defense
- It induces immune tolerance and immune homeostasis protecting against both allergic and autoimmune diseases
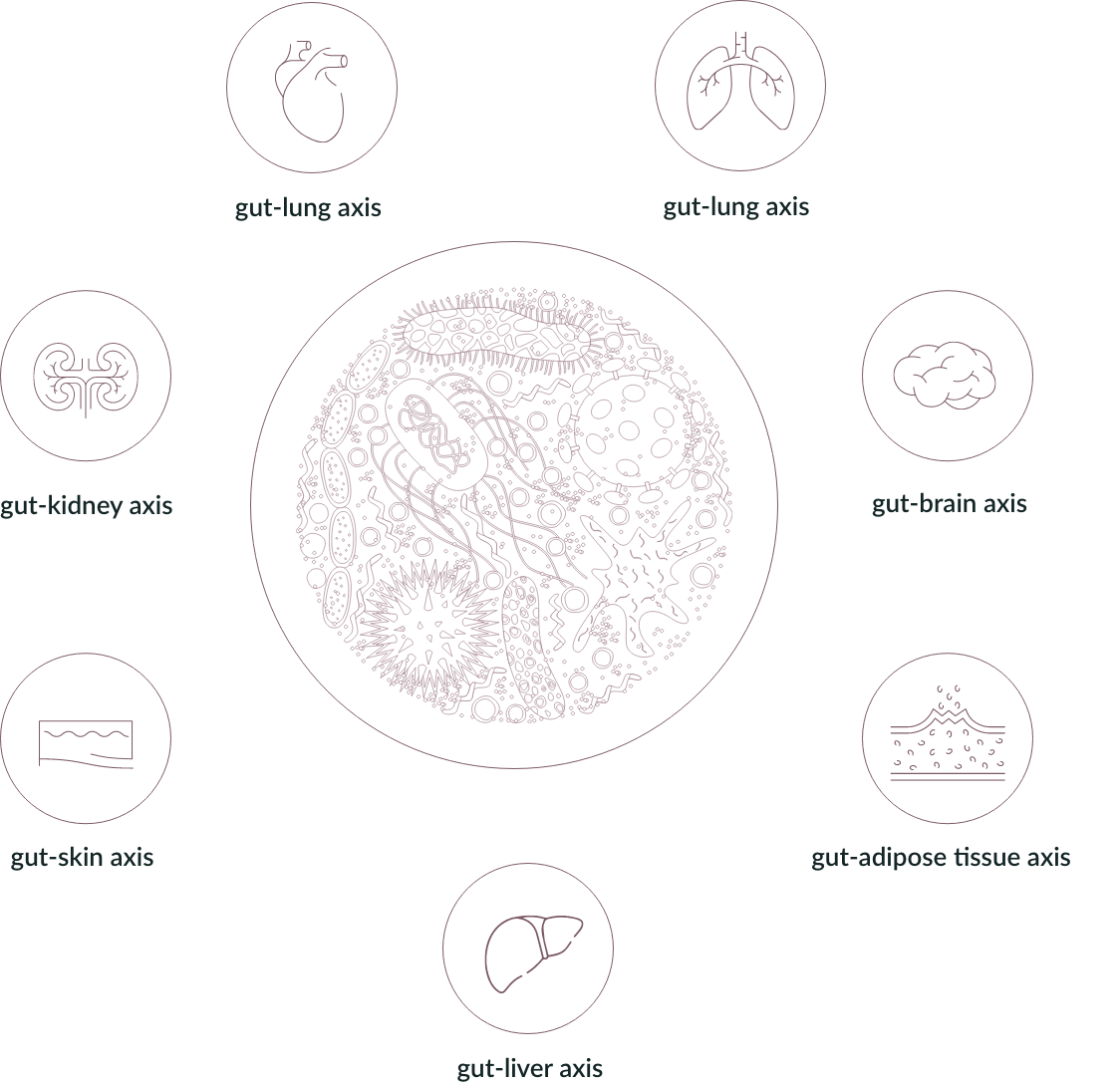
- It produces metabolites, including short-chain fatty acids that affect functioning of other organs and systems via the following axes: microbiome → gut → brain,
microbiome → gut → lungs,
microbiome → gut → skin,
microbiome → gut → adipose tissue,
microbiome → gut → liver.
Microbiota affects the functioning of other organs through the intestinal (gut) axes

Dysbiosis means microbiota imbalance
- Loss of biodiversity and “beneficial” bacteria
- Overgrowth of pathogenic bacteria
Microbiota homeostasis
Dysbiosis might cause medical conditions
- ALLERGY
food allergy, atopic dermatitis, rhinitis, asthma - METABOLIC DISEASES
obesity, fatty liver, type 2 diabetes, hypercholesterolaemia, atherosclerosis - OSTEOPOROSIS, OSTEOPENIA
- BRAIN DISEASE
autism, ADHD, depression and others
- CANCERS
- AUTOIMMUNE DISEASES
type 1 diabetes, MS, thyroid disease - ACUTE AND CHRONIC INFECTIONS
- GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS
diarrhea, constipation intestinal colic, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease
Cukrowska B. Znaczenie programowania mikrobiotycznego w rozwoju przewlekłych chorób nieinfekcyjnych. Standardy Medyczne. Pediatric 2016. 13. 10.-1028
Challenge
Dysbiosis (microbiological imbalance) caused by a disturbance in the composition of the microbiome and its functional activity
Solution
Probiotics modulate the composition of the intestinal microbiota, increasing the activity of bacteria that positively affect the health of the host and can eliminate intestinal dysbiosis and its effects.
Are you a company?
Learn more about our solutions.
Visit nordicbiotic.com
